Introduction
The Sun, our nearest star, is an awe-inspiring celestial body that not only provides the Earth with light and warmth but also possesses the potential to unleash powerful and sometimes disruptive phenomena known as solar storms. These mesmerizing yet potentially hazardous events are caused by the Sun's dynamic nature, and understanding them is crucial for our technological civilization and space exploration endeavours.
What are Solar Storms?
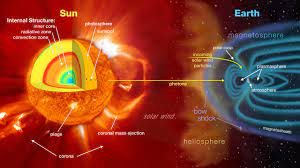
Solar storms, also called space weather events or solar flares, are explosive eruptions on the Sun's surface that release immense amounts of energy into space. These phenomena are primarily driven by the Sun's magnetic activity, which is a result of its rotating, fluid-like, and electrically conductive core. As the magnetic field lines get twisted and contorted, they can release energy in the form of solar flares, coronal mass ejections (CMEs), and solar energetic particles (SEPs).
Types of Solar Storms
Solar Flares:
Solar flares are intense bursts of electromagnetic radiation, primarily in the form of X-rays and ultraviolet light. They occur when magnetic energy stored in the Sun's atmosphere is suddenly released. These flares can be classified into different categories based on their X-ray intensity, with X-class flares being the most powerful and C-class flares being the weakest.
Coronal Mass Ejections (CMEs):
Coronal Mass Ejections are colossal plasma and magnetic field explosions from the Sun's corona into space. These massive clouds of charged particles can travel at speeds of several million miles per hour and have the potential to interact with the Earth's magnetic field.
Impact on Earth
While solar storms are a natural part of the Sun's behavior, they can significantly impact our technological infrastructure and communication systems on Earth. When a CME reaches our planet, it can cause a geomagnetic storm by interacting with the Earth's magnetic field. The resulting geomagnetic disturbances can induce electric currents in power lines, pipelines, and other long conductive systems, potentially leading to power outages and damage to transformers and electrical equipment.
Solar storms can also affect satellites in orbit around the Earth, experiencing increased drag due to the heightened atmospheric density during these events. This can lead to orbital decay and, in extreme cases, the premature end of satellite missions. Additionally, high-frequency radio communications and global positioning systems (GPS) can be disrupted by the enhanced ionization in the Earth's upper atmosphere caused by solar storms.
Spacecraft and astronauts outside the Earth's protective magnetosphere are vulnerable to the intense radiation associated with solar flares and SEPs. While modern space agencies take precautions to shield spacecraft and crew, solar storms remain a concern for long-duration space missions and interplanetary travel.
Space Weather Forecasting and Mitigation
Space weather forecasting has become vital to space exploration and safeguarding our technology-dependent society. Scientists and researchers use ground-based and space-borne observatories to monitor the Sun's activity and predict potential solar storms. The data collected from these observations are fed into sophisticated models to estimate the speed, direction, and intensity of approaching solar storms.
With improved forecasting capabilities, power grid operators can take preventive measures to minimize the impact of geomagnetic storms. Satellite operators can temporarily suspend non-essential operations and manoeuvres during periods of heightened solar activity, and astronauts can seek shelter within their spacecraft or return to Earth if necessary.
Conclusion
Solar storms are captivating celestial events that remind us of the immense power our closest star wields. While they can disrupt our technological infrastructure and space activities, our understanding of solar storms has significantly improved over the years. As we continue to explore space and rely more on technology, it becomes imperative to invest in research, observation, and forecasting to mitigate the potential impact of these fascinating yet formidable solar phenomena. With continued efforts, we can harness the power of knowledge to adapt to the Sun's rhythmic dance and protect ourselves and our technology from the mesmerizing yet occasionally hazardous beauty of solar storms.



Comments
Post a Comment